Specific Heat Capacity and Molar Heat Capacity
Specific Heat Capacity and Molar Heat Capacity: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Heat Capacity, Specific Heat Capacity, Molar Specific Heat Capacity & Heat etc.
Important Questions on Specific Heat Capacity and Molar Heat Capacity
The molar heat capacity of water at constant pressure is . When 1kJ of heat is supplied to 100g of water, which is free to expand, the increase in temperature of water is
During an adiabatic process, the pressure of a gas is found to be proportional to the cube of its absolute temperature. The ratio for the gas is . Find .
The SI unit of specific heat is .
Amongst object A and B, if the specific heat of object A is less than of object B, then
The specific heat capacity of any substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one unit substance by hundred degree.
The amount of heat required to increase the temperature of one kilogram of a material, by is called latent heat.
A cube of lead of at is supplied with a heat. Find the final temperature (in degree Celsius) of the lead cube. (Take, specific heat of lead is )
Calculate the heat energy (in joules) to raise the temperature of of water from to . (Take specific heat of water, )
If an ideal diatomic gas follows the process as shown in graph, where is temperature in and is volume in , then molar heat capacity for this process will be [in terms of gas constant ],
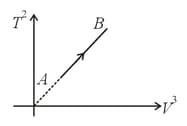
The number of degrees of freedom of a gas whose specific heat capacity at constant pressure is is
(universal gas constant )
The ends of a uniform metal rod of length and area of cross-section are maintained at and . At the mid-point of the rod, heat is supplied at a constant rate of . If the temperature gradient on the higher temperature side of the rod in steady state is , then the value of is (Thermal conductivity of the metal )
What is the SI unit of heat?
Define heat. What is its SI unit?
For next 2 question please follow the same
Molar heat capacity of an ideal gas in the process constant is given by
An ideal diatomic gas with occupies a volume V1 at a pressure P1 . The gas undergoes a process in which the pressure is proportional to the volume. At the end of the process the rms speed of the gas molecules has doubled from its initial value.
The molar heat capacity of the gas in the given process is
Specific heat capacity of a substance depends on the mass of the substance.
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of the whole substance through is called the _____. (heat capacity/specific heat capacity)
Find the heat energy released from the liquid in cooling kg of liquid from to . While the specific heat of the liquid is joule/kg .
To increase the temperature of kg of fluid from to calories of heat are required. Find the specific heat of the liquid.
a. in calories
b. in joules.
Mass of same material of two solids is and respectively. Whose temperature will increase more after heating.
How many joule is equal to calorie?
